The original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e 0 if demand shifts from d 0 to d 1 the new equilibrium would be at e 1 unless a price ceiling prevents the price from rising.
Product supply and demand graph with floor and ceiling.
Taxation and deadweight loss.
First let s use the supply and demand framework to analyze price ceilings.
Typically the supply side effects dominate the demand side ones when the government creates a black market.
Tax incidence and.
Remember changes in price do not cause demand or supply to change.
The market price remains p and the quantity demanded and supplied.
In other words they do not change the equilibrium.
A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.
At price pf consumer demand is qd more than q due to downward sloping demand curve and producers supply is qs less than q due to upward sloping supply curve.
This is the currently selected item.
Price ceilings and price floors can cause a different choice of quantity demanded along a demand curve but they do not move the demand curve.
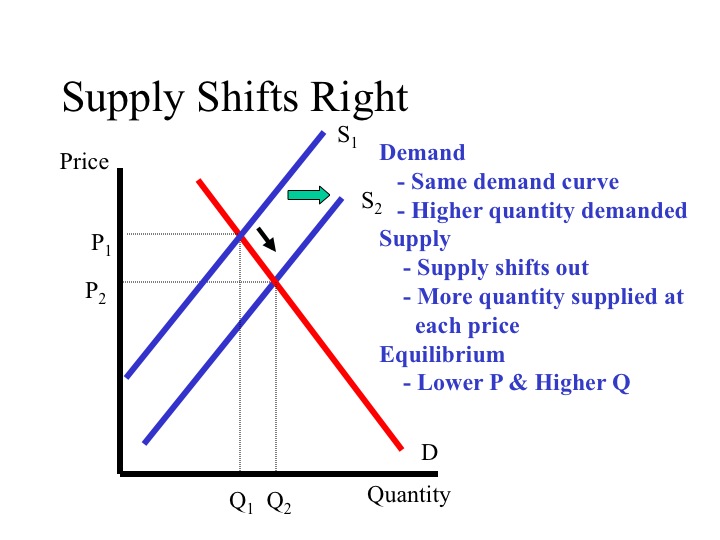
Similarly a drop in demand means the downward sloping demand curve will shift to the left.
The government establishes a price floor of pf.
It tends to create a market surplus because the quantity supplied at the price floor is higher than the quantity demanded.
Price and quantity controls.
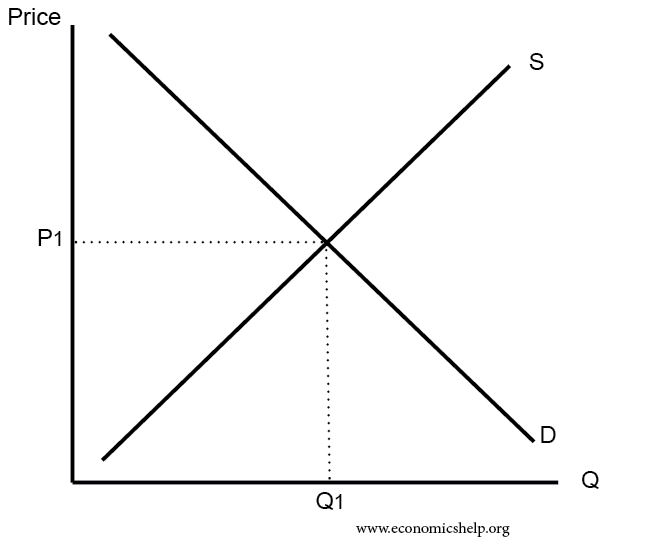
The quantity supplied at the market price equals the quantity demanded at that price.
When prices are established by a free market then there is a balance between supply and demand.
Taxes and perfectly elastic demand.
A price floor is a minimum price enforced in a market by a government or self imposed by a group.
The effect of government interventions on surplus.
Price ceilings and price floors.
If the price is not permitted to rise the quantity supplied remains at 15 000.
A price ceiling example rent control.
However the non binding price floor does not affect the market.
Demand curve is generally downward sloping which means that the quantity demanded increase when the price decreases and vice versa.
The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external.
Black market supply and demand illustration 2.
What will be the price and quantity of bread purchased.
A government decides to set a price ceiling on bread of 2 40 so that bread is affordable to the poor.
Price controls can cause a different choice of quantity supplied along a supply.
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.
Taxes and perfectly inelastic demand.
A price ceiling is a legal maximum price that one pays for some good or service.
A drop in supply means the upward sloping supply curve will shift to the left.
The conditions of demand and supply are given in the table below.